Create a Gateway environment¶
Each Gateway environment definition contains details related to a specific Gateway. You can create a Gateway environment that includes VHosts using either one of the following methods.
Option 1: Create a Gateway environment via the Admin Portal¶
This will start WSO2 API Manager in the all-in-one mode, which includes the default Gateway as well.
-
Sign in to the Admin Portal.
https://<hostname>:9443/adminExample:
https://localhost:9443/adminLet's use
adminas your username and password to sign in. -
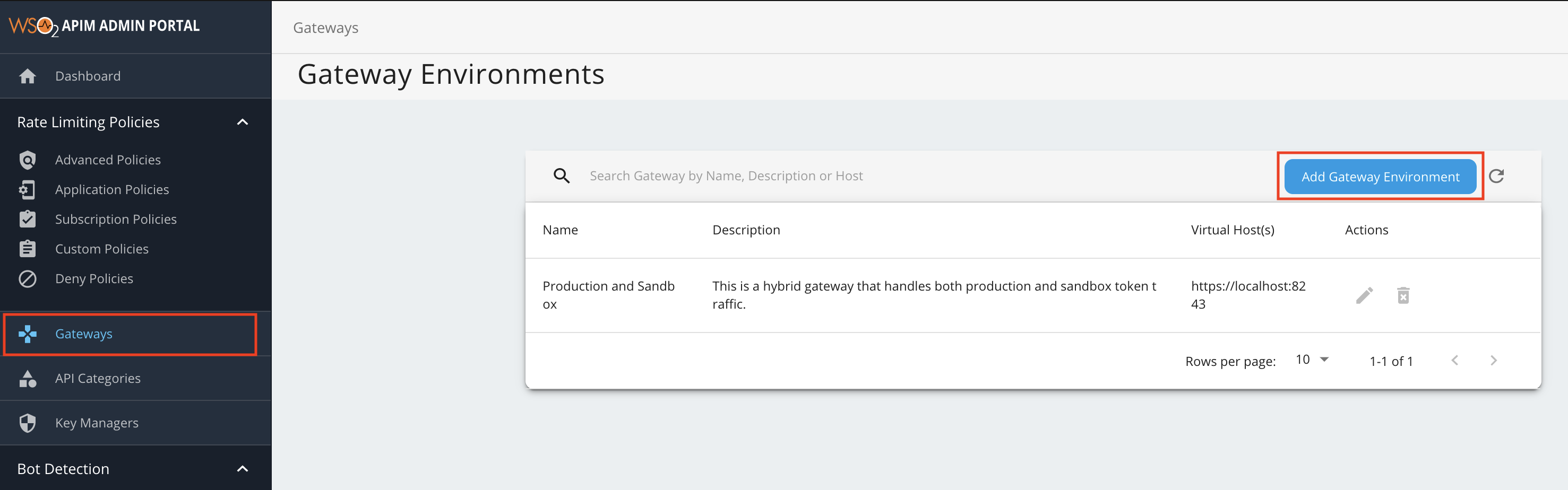
Add a new Gateway Environment.
- Click Gateways, and then click Add Gateway Environment.
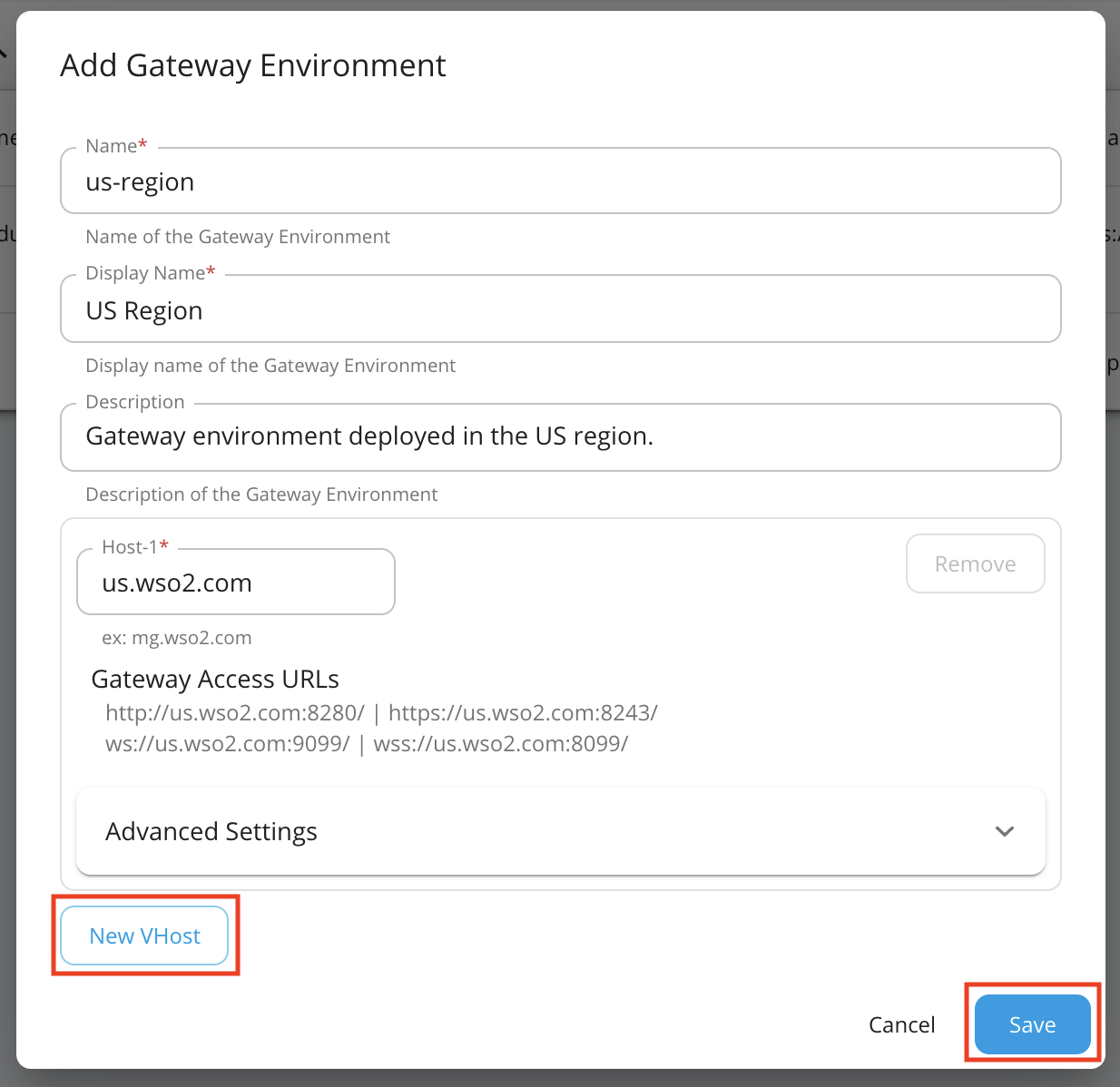
- Enter a name, display name, description, and a virtual host.
The virtual hosts will define each of the custom hostnames. It is mandatory to specify a VHost when you create a Gateway environment.
Environment Display Name Description Virtual Host us-region US Region Gateway environment deployed in the US region. us.wso2.com
Note
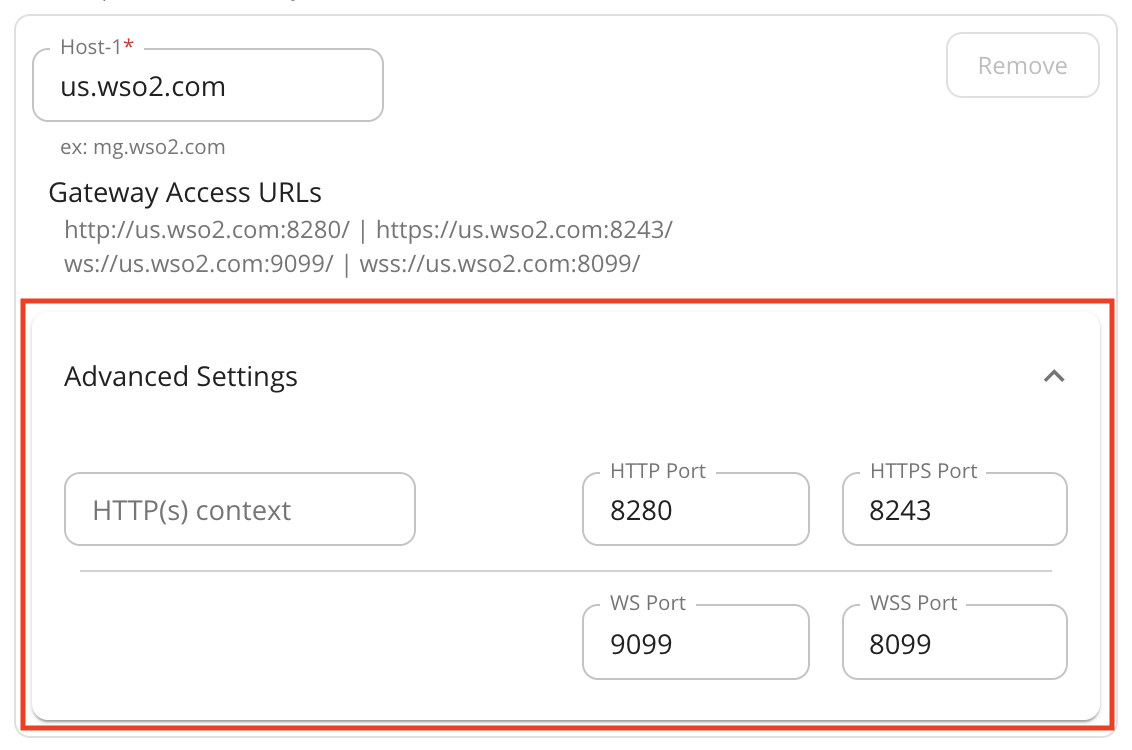
- You can change the ports of each protocol of the Virtual Host and add an optional HTTP(s) context.
- Let's add
gatewayas the HTTP(S) context for the Virtual Hostus.wso2.com. - Add another virtual host
foods.comby clicking New VHost and click Save to save the environment.
Option 2: Create a Gateway environment using the configuration file¶
Follow the instructions below to use the deployment.toml file, which is the central configuration file, to configure a Gateway environment that consists of virtual hosts:
-
Open to the
<APIM-HOME>/repository/conf/deployment.tomlfile. -
Create a Gateway environment.
Create a Gateway environment with the following Gateway configurations, which include us.wso2.com and foods.com as the custom VHosts and food as the custom context.
Note
- When the WSO2 API Manager server is running, the Gateway environments, which you added via the
deployment.tomlfile, are displayed in the Gateway environments list page in the Admin Portal in read-only mode. - Therefore, ensure to add the VHosts that correspond to the Gateway at the time of adding the Gateway environment itself.
- If a VHost is not defined, the default VHost details are assigned to the Gateway environment.
- It is not mandatory to specify a context for the VHost.
[[apim.gateway.environment]]
name = "us-region"
display_name = "US Region"
type = "hybrid"
display_in_api_console = true
description = "Gateway environment deployed in the US region."
show_as_token_endpoint_url = true
service_url = "https://localhost:${mgt.transport.https.port}/services/"
username= "${admin.username}"
password= "${admin.password}"
ws_endpoint = "ws://localhost:9099"
wss_endpoint = "wss://localhost:8099"
http_endpoint = "http://localhost:${http.nio.port}"
https_endpoint = "https://localhost:${https.nio.port}"
websub_event_receiver_http_endpoint = "http://localhost:9021"
websub_event_receiver_https_endpoint = "https://localhost:8021"
[[apim.gateway.environment.virtual_host]]
ws_endpoint = "ws://us.wso2.com:9099"
wss_endpoint = "wss://us.wso2.com:8099"
http_endpoint = "http://us.wso2.com/gateway"
https_endpoint = "https://us.wso2.com/gateway"
websub_event_receiver_http_endpoint = "http://us.wso2.com:9021"
websub_event_receiver_https_endpoint = "https://us.wso2.com:8021"
[[apim.gateway.environment.virtual_host]]
ws_endpoint = "ws://foods.com:9099"
wss_endpoint = "wss://foods.com:8099"
http_endpoint = "http://foods.com:8280"
https_endpoint = "https://foods.com:8243"
websub_event_receiver_http_endpoint = "http://foods.com:9021"
websub_event_receiver_https_endpoint = "https://foods.com:8021"
This will start WSO2 API Manager in the all-in-one mode, which includes the default Gateway as well.
Note
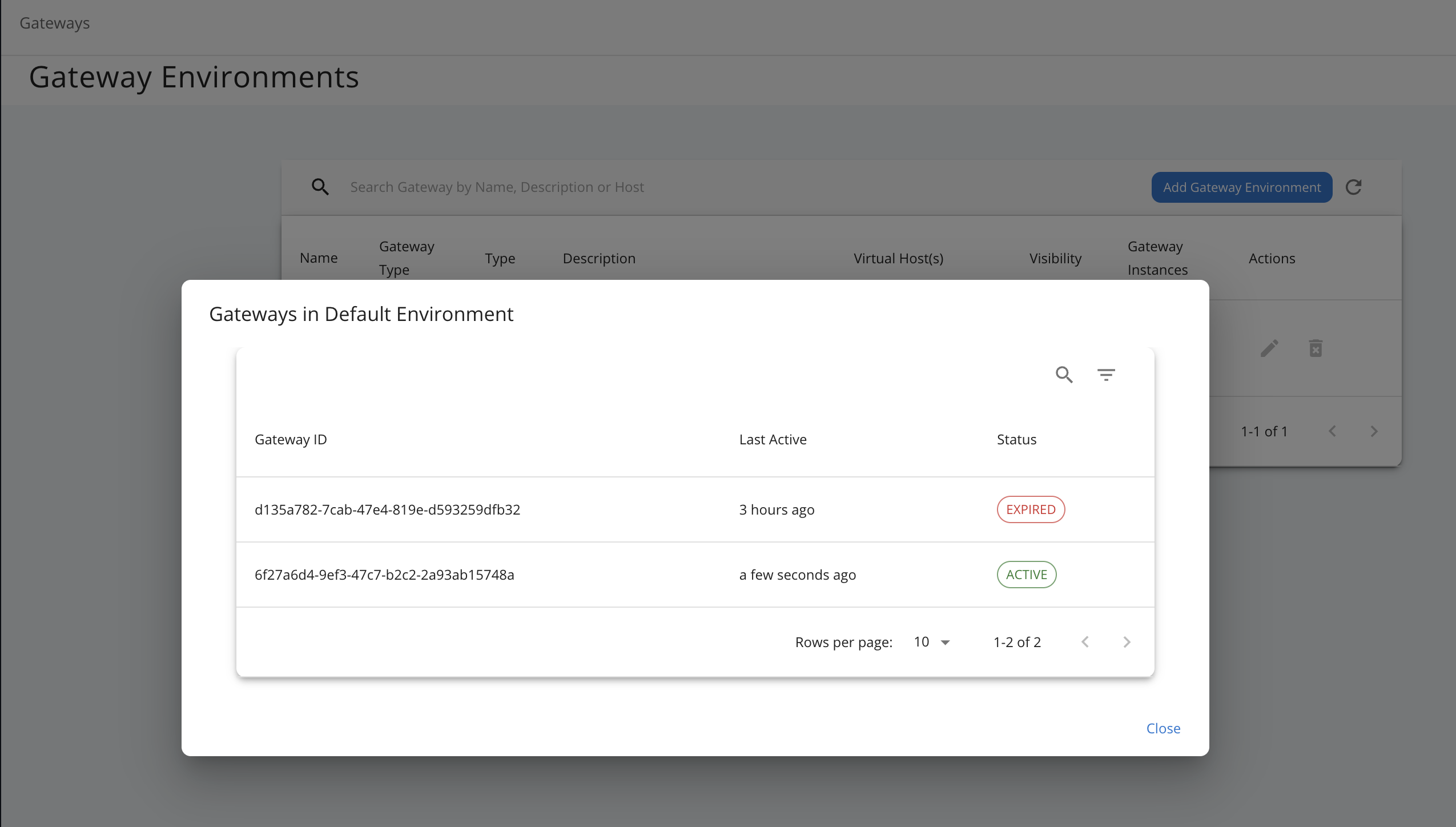
Once the Gateway environment is set up, you can observe the active Gateway instances registered under the created environment, as shown in the image below. If a Gateway instance shows an expired status, it means the instance has not sent a heartbeat signal within the expected time interval and is considered inactive or unreachable.