Enforce GraphQL Query Limits¶
GraphQL APIs allow clients to request complex queries with nested fields and relationships. Without protection, backends are vulnerable to DoS attacks caused by the execution of malicious and complex queries. WSO2 API Manager introduces a Static Query Analyzer at the Gateway to secure GraphQL APIs by detecting and blocking complex queries before they reach the backend.
How the Gateway Enforces GraphQL Limits¶
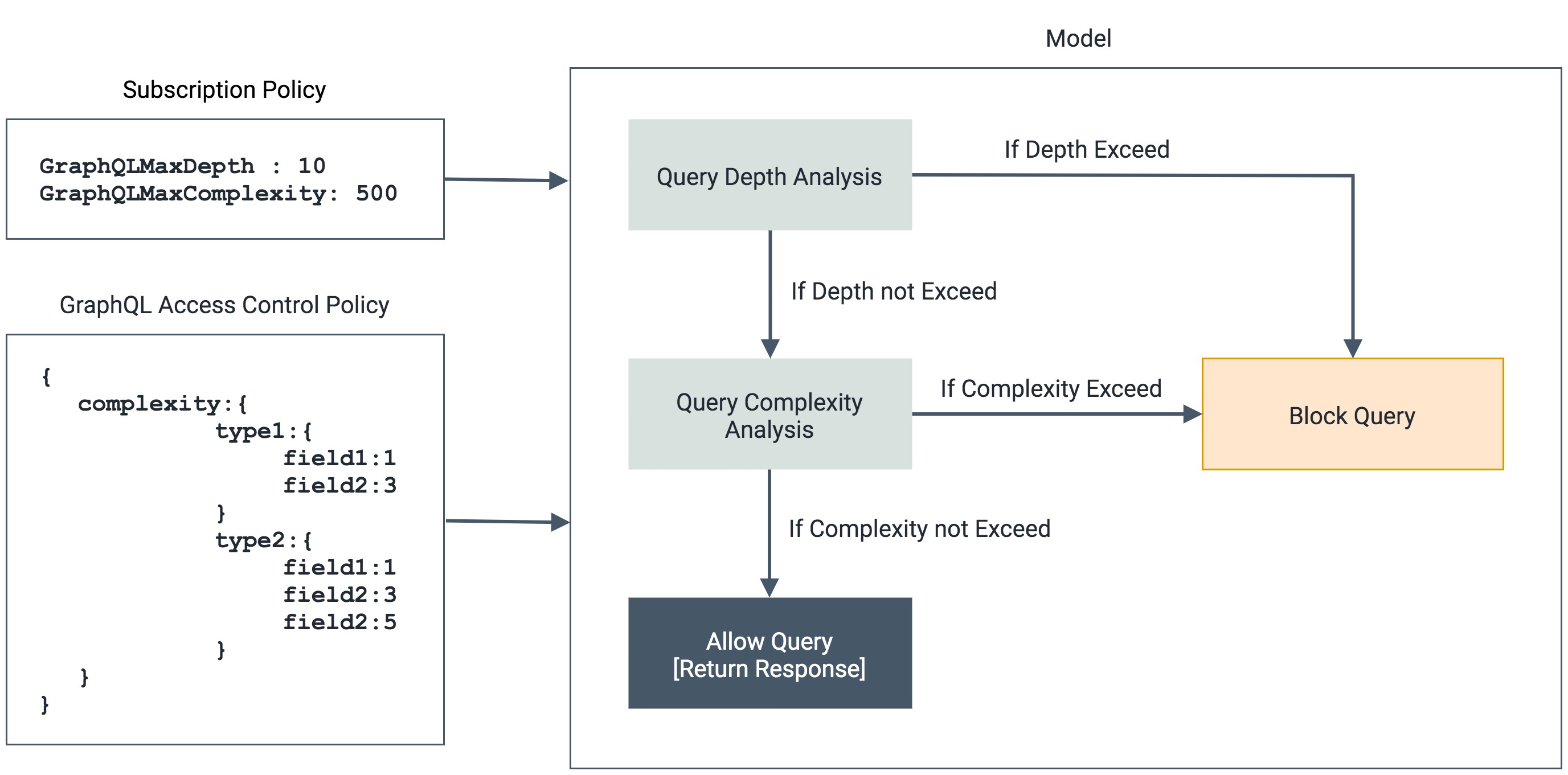
When a GraphQL API request arrives at the Gateway, the Static Query Analyzer evaluates the query against predefined limits configured in the subscription policy. The Gateway enforces two types of limits:
Query Depth Limitation¶
Query depth limitation prevents cyclic relationships and unbounded nesting in GraphQL queries. Since GraphQL schemas often have circular relationships, the depth can grow without bounds, allowing bad actors to construct expensive nested queries.
The Gateway calculates the depth of the requested query and compares it against the GraphQL Max Depth value configured in the subscription policy. If the query depth exceeds the configured maximum, the Gateway rejects the request before it reaches the backend.
Example:
query{ # depth 0
allFilms{ # depth 1
id # depth 2
Species{
id # depth 3
films{
title # depth 4
planets{
id # depth 5
residents{
eyeColor # depth 6
films{
director # depth 7
producers
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
# depth value of query : 7
If an API is configured with a Max Depth value of 5, the above query with depth 7 will be rejected by the Gateway.
Query Complexity Limitation¶
Limiting only the depth of a query is not sufficient to protect a GraphQL service from complex queries. Some fields in a GraphQL schema are more costly to compute than others. Query complexity limitation addresses this by assigning complexity values to each field in the schema, describing the computation cost of resolving that particular field.
Field Complexity Values:
- Fields that call expensive services to resolve should have high complexity values
- Fields that are easy to resolve (inexpensive operations) should have low complexity values
- If no complexity is defined for a field, it defaults to a value of 1
The Gateway calculates the total complexity of the query and compares it against the GraphQL Max Complexity value configured in the subscription policy. A query is blocked if its calculated complexity exceeds the specified maximum.
Complexity Calculation Examples:
Without arguments (simple addition):
query {
allFilms{ # complexity 1
id # complexity 3
title # complexity 1
planets { # complexity 2
climate # complexity 1
}
}
}
# total complexity = 1 + 2 + 1 + 3 + 1 = 8
With arguments (multiplication):
query {
allFilms(first: 5){ # complexity 1
id # complexity 1
title # complexity 1
planets(first: 2) { # complexity 1
climate # complexity 1
}
}
}
# total complexity = ((( 1 + 1 ) * 2 ) + 1 + 1 + 1 ) * 5 = 35
Nested with multiple arguments:
query {
allFilms(first: 5){ #complexity 1
id #complexity 3
title #complexity 1
planets(first: 2) { #complexity 2
climate #complexity 3
films(first: 5) { #complexity 1
createdAt #complexity 1
director #complexity 1
}
}
}
}
# total complexity = ((((((1 + 1 + 1)* 5)+ 3 + 2 )* 2)+ 1 + 3 + 1)* 5) = 225
Request Flow¶
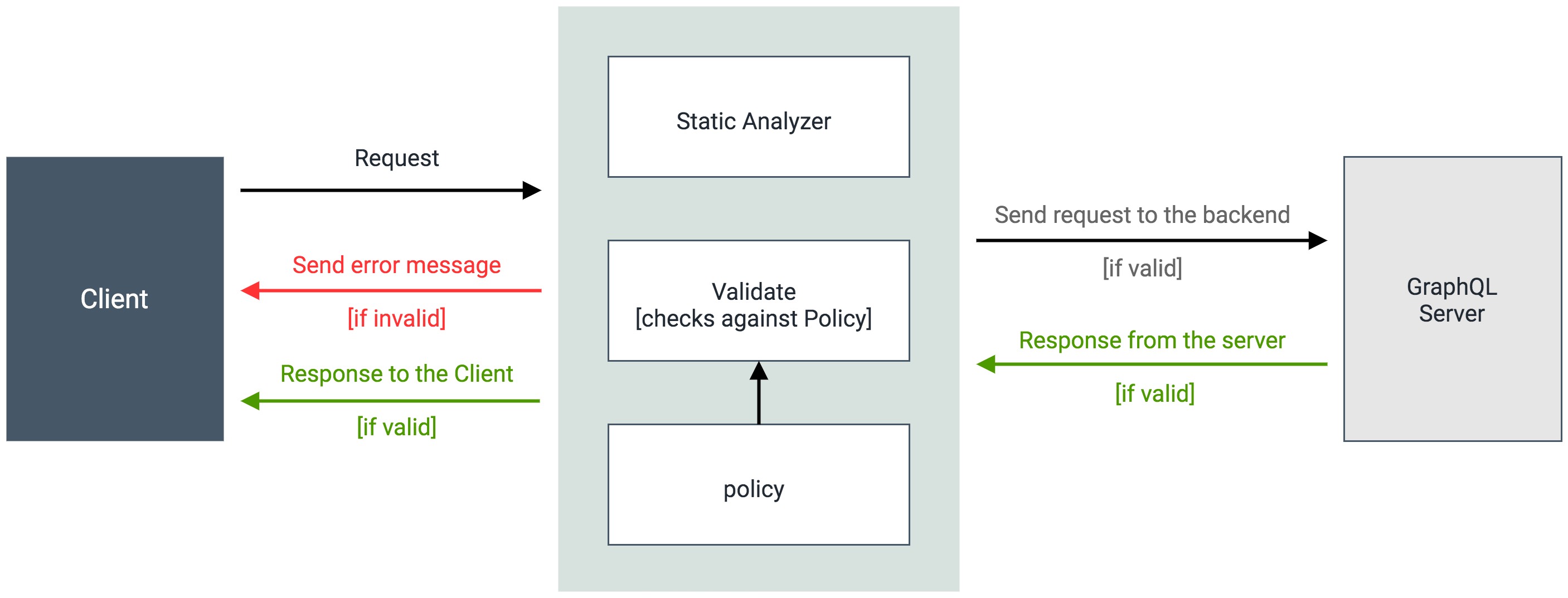
The following diagram illustrates how the Gateway enforces GraphQL query limits at runtime:
The overall request/response flow:
Enforcement Steps:
- GraphQL API request arrives at the Gateway
- Static Query Analyzer extracts the query from the request
- Gateway calculates query depth and complexity values
- Gateway compares calculated values against subscription policy limits (Max Depth and Max Complexity)
- If either limit is exceeded, Gateway rejects the request with an error response
- If within limits, Gateway forwards the request to the backend
Configuration¶
GraphQL query limits are configured through subscription policies:
- GraphQL Max Depth: Maximum allowed depth for queries
- GraphQL Max Complexity: Maximum allowed complexity for queries
- Field Complexity Values: Custom complexity values for individual fields in the schema
Publishers can customize field complexity values for their GraphQL APIs to accurately reflect the computational cost of resolving each field.
See Also¶
- For more information on creating and configuring graphql query limits in subscription level policies, see Managing Subscription Policies