WSO2 Key Manager¶
Production API deployments face authentication and authorization challenges: token management complexity, OAuth application lifecycle overhead, inconsistent security policies across providers, and the need for enterprise-grade access control systems.
WSO2 Key Manager serves as the authentication and authorization service (STS) that the API Gateway and AI Gateway use to secure API runtimes within the WSO2 API Manager platform.
As the central security authority for API access, it enables:
- Application Developers: Generate keys and dynamically register client applications using available key managers for their tenant
- API Developers: Control which key managers are allowed to access each API through API-level configuration
- Administrators: Configure and manage multiple key managers via the Admin Portal for enterprise integration
- Token Lifecycle Management: Complete token generation, validation, renewal, and revocation workflows
- Multi-Provider Support: Built-in key manager with third-party authorization server integration
- Standards Compliance: Full OAuth2, OpenID Connect, SAML, and Kerberos protocol support
Architecture¶
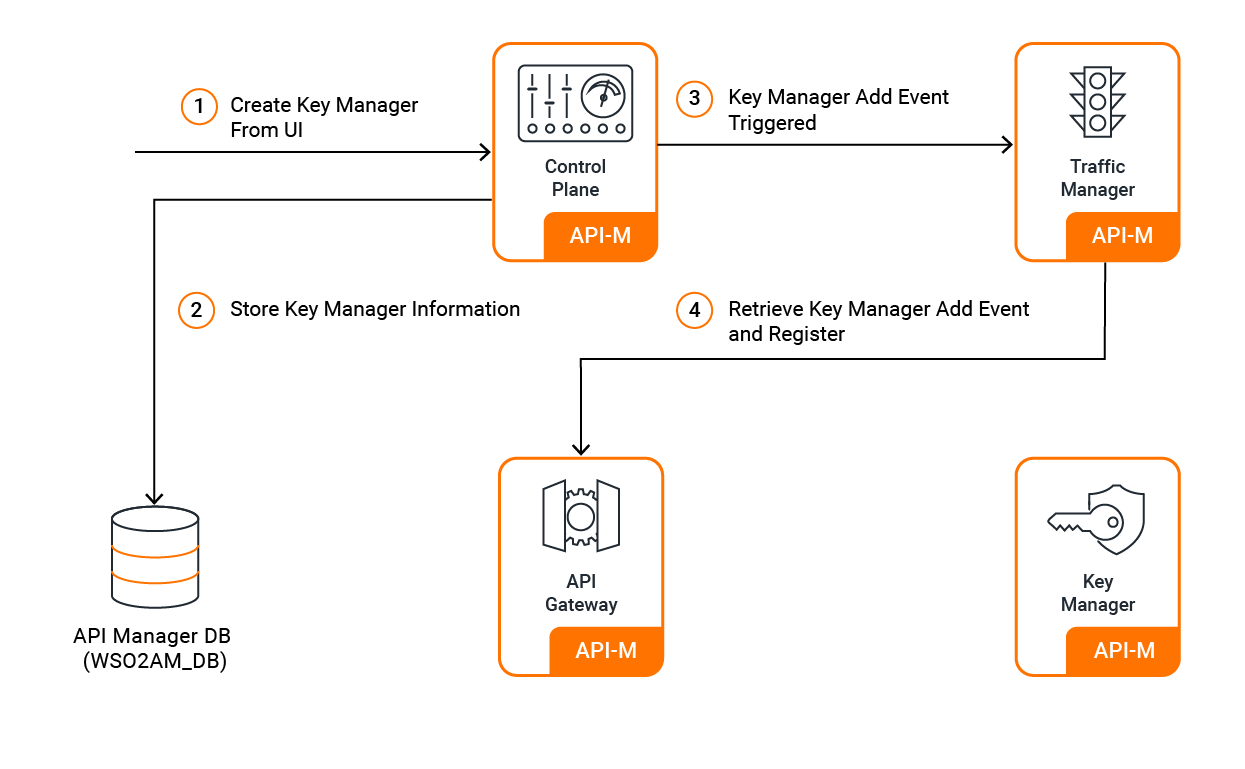
WSO2 API Manager supports multiple key managers within a single tenant, enabling organizations to integrate various authorization servers simultaneously. Administrators can configure different key managers via the Admin Portal, making them available for application developers and API creators.
When an administrator adds a key manager through the Admin Portal:
- Persistence: The configuration is stored in the API Manager database
- Event Propagation: An event is triggered to the Traffic Manager
- Gateway Registration: The Gateway receives the event and registers the new key manager
- Tenant Availability: The key manager becomes available for all APIs within that tenant
Application Developer Experience¶
Key Generation: Application developers see all configured key managers as options when generating keys for their applications. No additional configuration is required - all available key managers are automatically presented as choices.
Dynamic Registration: Applications can be dynamically registered with any key manager that supports consumer application creation, subject to the key manager's validation requirements.
API Developer Control¶
Key Manager Restrictions: API developers can configure their APIs to restrict access to specific key managers based on security requirements. This allows fine-grained control over which authentication providers can access each API.
Gateway Integration: The API Gateway works with key managers to authenticate requests and validate tokens:
JWT Tokens: For JWT tokens, the Gateway retrieves issuer details from the token to identify the relevant key manager. If the key manager is not enabled for the API, validation fails.
Non-JWT Tokens: For opaque tokens, validation occurs based on the token handling options configured in the relevant key manager.
Role-Based Key Manager Restrictions¶
Administrators can implement role-based access control for key managers:
ALLOW Permission: Only users with specified roles can use the key manager for key generation DENY Permission: Users with specified roles cannot use the key manager for key generation
Note
- Exercise caution when restricting key managers to avoid scenarios where users lose access
- A key manager can have either whitelist (ALLOW) or blacklist (DENY) permissions, not both
- Keys generated before access restriction remain valid until expiration
Built-in Key Manager¶
The Built-in Key Manager provides comprehensive OAuth2 and OpenID Connect capabilities without requiring external dependencies. It handles all authentication and authorization operations internally within the API Manager platform.
Use Built-in Key Manager when you need¶
- Self-contained API Manager deployment without external dependencies
- Full control over token generation and validation policies
- Simplified deployment and maintenance requirements
Built-in Key Manager Features¶
OAuth2 Token Management
- JWT Access Tokens: Self-contained tokens with embedded claims for gateway validation
- Token Persistence: Optimized storage strategies for JWT and opaque tokens
- Token Expiration: Configurable token lifetimes and automatic cleanup
- Token Revocation: Immediate token invalidation for security incidents
Grant Type Support
- Authorization Code Grant: Web application authentication flows with user consent
- Client Credentials Grant: Service-to-service authentication without user interaction
- Password Grant: Direct credential authentication for trusted applications
- Refresh Token Grant: Token renewal without re-authentication
- JWT Bearer Grant: Token exchange using signed JWT assertions
- SAML Extension Grant: SAML assertion-based authentication
- Kerberos OAuth2 Grant: Windows authentication integration
- NTLM Grant: Windows domain authentication support
Security
- Token Encryption: Encrypt tokens at rest and in transit
- OAuth Key Hashing: Secure storage of client credentials
- HMAC Token Validation: Additional token integrity verification
Application & Client Management
- Out-of-Band OAuth Clients: Register applications outside standard flows
- OAuth Application Federation: Cross-tenant application sharing
Identity Integration
- OpenID Connect: User profile information retrieval with standard claims
Third-Party Key Manager Integration¶
Third-Party Key Manager Integration enables organizations to leverage existing enterprise identity providers while maintaining centralized API access control through WSO2 API Manager.
Use Third-Party Key Managers when you need¶
- Integration with existing enterprise identity infrastructure
- Compliance with organizational authentication policies
- Centralized user management across multiple systems
- Specialized authentication capabilities
Supported Third-Party Key Managers¶
Enterprise Identity Providers
- WSO2 Identity Server: Full-featured identity and access management platform
- WSO2 Identity Server 7.x: Latest identity server with enhanced capabilities
- Keycloak: Open-source identity and access management solution
- Okta: Cloud-based identity service integration
Custom Integration
- Custom Key Manager: Build connectors for proprietary authorization servers
- Global Key Manager: Cross-tenant key manager configuration
Cloud Provider Integration
- Azure AD Key Manager: Microsoft Azure Active Directory integration
- ForgeRock: ForgeRock Identity Platform integration
Getting Started¶
Choose Your Key Manager Strategy¶
Built-in Key Manager - Self-Contained Deployment Start here for simplified deployment without external identity provider dependencies.
- Deploy API Manager with built-in key manager capabilities
- Configure OAuth2 grant types for your application types
- Set up token policies and security configurations
Third-Party Integration - Enterprise Identity Start here to integrate with existing enterprise identity infrastructure.
- Assess current identity provider capabilities and requirements
- Configure appropriate third-party key manager connector
- Test authentication flows and token validation
- Gradually migrate applications to centralized authentication
Hybrid Approach - Mixed Environment Start here for organizations with diverse authentication requirements.
- Configure built-in key manager for internal applications
- Add third-party key managers for enterprise systems
- Configure API-level key manager restrictions based on security requirements
Best Practices¶
Start with JWT Tokens for Production¶
Always use JWT access tokens in production deployments. JWT tokens enable gateway-side validation without key manager round-trips, significantly improving performance and reducing latency. Start with standard JWT configurations and customize claims as needed for your applications.
Implement Token Lifecycle Management Early¶
Configure appropriate token expiration and implement token revocation capabilities from day one. Set conservative token lifetimes initially and monitor usage patterns to optimize refresh cycles. This prevents token sprawl and security incidents.
Design Client Applications for Proper Token Management¶
Client applications should implement proper token lifecycle management by persisting access tokens and refresh tokens rather than requesting new tokens for every API call. Store tokens securely and use refresh tokens to obtain new access tokens when they expire. This reduces load on the key manager and improves application performance.
Optimize Token Persistence for High-Volume Deployments¶
For deployments with millions of users and high token generation rates, consider enabling JWT token persistence optimization. This approach uses JWT tokens without persisting them in the database, significantly improving performance for short-lived tokens. Enable persistence optimization when you have: - High concurrent user logins and token generation - Short token lifespans (recommended for this optimization) - Need to reduce database load and improve TPS (Transactions Per Second)
Choose Grant Types Based on Application Architecture¶
Map OAuth2 grant types to your application types: use client credentials for service-to-service, authorization code for web applications, and password grant only for highly trusted internal applications. Avoid the implicit grant type in production environments.
Implement Comprehensive Scope Management¶
Use OAuth2 scopes to implement fine-grained access control from the beginning. Design your scope hierarchy to match your API resource structure and business permissions. Implement scope whitelisting to prevent privilege escalation.
Next Steps¶
Choose your path based on your authentication requirements:
- OAuth2 Grant Types Overview - For understanding authentication flows and choosing appropriate grant types
- Configure Third-Party Key Managers - For integrating with existing enterprise identity providers